Enterprises across the globe are increasingly adopting ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems to streamline business operations and reduce unnecessary expenses. ERP systems enhance transparency across departments and provide stakeholders with actionable insights, enabling data-driven decision-making. Since ERP implementation involves significant investment and can directly impact business success, this article will explore the key stages of the ERP implementation process and its lifecycle.
What is an ERP?
ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. It is a type of software used by organizations to manage and integrate the core functions of their business (Financial Management, Supply Chain Management, Human Capital Management, project management, inventory management, etc.).
What is an ERP Lifecycle?
The ERP lifecycle refers to the entire process of planning, implementing, maintaining, and eventually upgrading or replacing an ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system.
What are the Different ERP Implementation Phases?
ERP implementation is a complex process that can take several months, as it involves integrating critical business functions such as financial management, human resources, sales, and manufacturing. These processes become automated, providing stakeholders with a real-time view across departments, which boosts productivity and operational efficiency. To maximize your return on investment, it’s essential to understand the various stages of the ERP lifecycle.
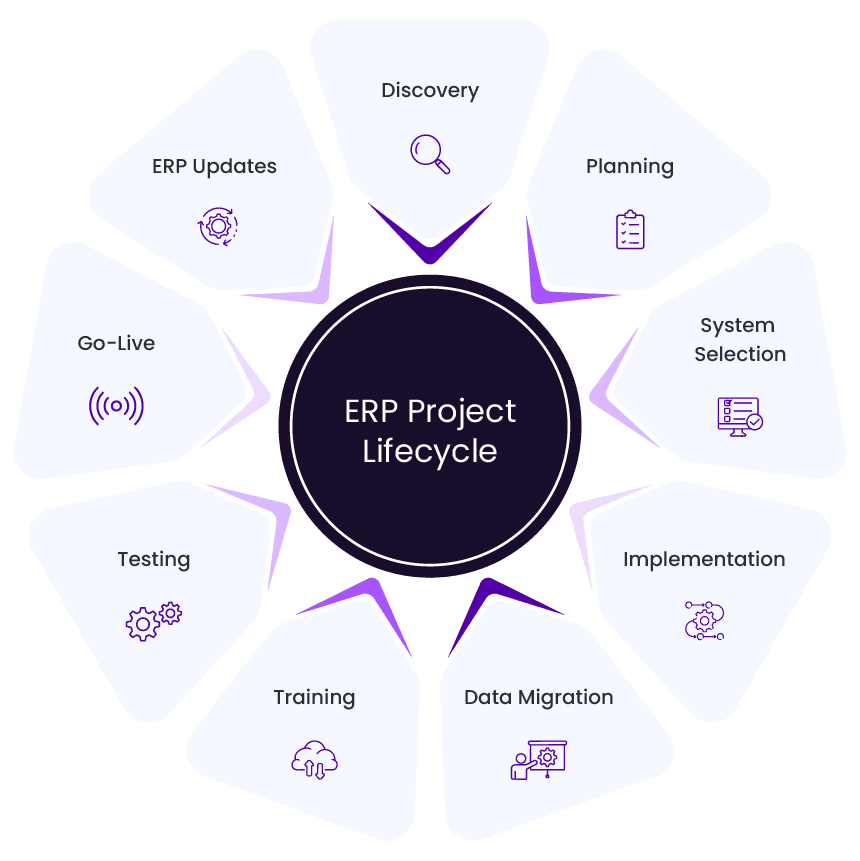
Key Stages of ERP Implementation Project Lifecycle
Discovery and Planning
Every business has its own unique set of requirements, and with numerous ERP options available in the market, selecting the right solution can be daunting. To streamline the selection process, organizations typically form a project team that includes a project manager and representatives from the departments that will use the system. This team is responsible for developing a detailed understanding of current challenges, such as process inefficiencies and specific requirements for ERP software.
If the organization has already developed a business case for ERP, it may have outlined broad goals such as faster financial closing, improved operational insights, or preparing for an IPO. These goals can guide a more in-depth analysis, including documentation of existing workflows and process gaps, and help shape the system’s development. During this phase, the team may also evaluate, select, and acquire the ERP system, as they now have a clearer understanding of organizational needs.
System Selection
Now that your requirements are clearly defined, it’s time to select the cloud ERP system that best fits your unique business needs. The decision-making process should begin by identifying key details, including the specific pain points within your operations and your existing technology stack.
Conducting a gap analysis helps uncover process intricacies and operational challenges that may require either customization of the ERP software or adjustments to your workflows to better align with the system’s capabilities. The project team can then present these gaps to the ERP vendor or implementation partner and collaborate to identify the most effective solutions.
Implementation
In this phase, the ERP software is configured—and customized to accommodate current business processes where needed. It’s also the stage where integrations are developed to connect the ERP system with any existing business applications that will continue to be used alongside it. The goal is to ensure smooth communication across systems and a seamless flow of data, so the organization can operate efficiently from day one.
Data Migration
After your ERP system is installed, the next critical step is migrating your company data into the new system. This begins with cleaning the data—removing any errors, duplicates, or outdated information—and then transferring it into the new ERP database. This typically includes essential records such as customer and vendor details, item master files, bills of materials, routing instructions, and general ledger account structures. As you approach the go-live phase, current transactional data is also converted or transferred to ensure a smooth transition.
Data migration can be a complex process, especially when dealing with information from multiple systems that use different formats or contain inconsistent records. That’s why it’s important for the project team to carefully decide which data is truly necessary to move. Migrating only relevant and accurate data—rather than attempting to import everything—helps prevent issues down the line and sets up a clean foundation for the new ERP system.
ERP System Training and Change Management
Investing in an ERP system is a strategic move aimed at boosting employee productivity and improving overall operational efficiency. However, these benefits can only be realized when end users fully adopt and utilize the new system. To support this, it’s essential to involve Subject Matter Experts (SMEs)—such as members from the IT or finance teams—early in the ERP implementation process. These individuals should receive in-depth training so they can serve as internal trainers and become the go-to resources for other employees once the system is live.
Additionally, all end users must be trained to carry out their specific responsibilities within the new ERP environment. Tailored training ensures that every employee understands how to navigate the system effectively, helping to minimize resistance to change and drive a smoother transition. Change management efforts should focus on communication, support, and ongoing learning to ensure long-term success.
ERP Testing and Validation
This stage is one of the most critical in the ERP implementation lifecycle. It’s where everything comes together to ensure the system is not only functional but also aligned with the business’s day-to-day needs. The primary goal here is to identify and fix any errors before the system goes live, minimizing risks and ensuring a smoother rollout.
A structured testing plan should be created, covering unit tests, integration tests, and user acceptance testing (UAT). Employees should be encouraged to engage in UAT, using the system as they would post-launch, which helps identify usability gaps early. Equally important is validating the accuracy of migrated data and ensuring it reflects what existed in the old system. Engaging IT and business stakeholders in this step not only boosts confidence in the system but also ensures that what’s being delivered truly meets the needs of its users. Proper testing not only ensures successful implementation but also lays the foundation for long-term success.
Go-Live and Stabilization
This is the moment your ERP journey becomes real—the system officially goes live. It’s an exciting yet delicate phase where all the planning, configuration, testing, and training culminate in actual day-to-day use. While the groundwork has been laid, it’s normal for unexpected issues or questions to arise as users start interacting with the live system.
To ensure a smooth transition, your ERP project team must be on standby to support employees, answer questions, and resolve any hiccups promptly. Stabilization is about fine-tuning—monitoring system performance, user adoption, and ironing out any remaining glitches. With the right support from the ERP implementation team, your organization can move from go-live anxiety to steady operational confidence, unlocking the full value of your ERP investment.
Maintenance and ERP Updates
Implementing an ERP system isn’t a one-time project that wraps up at go-live. It’s an ongoing journey. As your business evolves and industry regulations shift, your ERP system must keep pace. That’s why ERP vendors regularly release updates, enhancements, and new features designed to meet changing demands and improve system capabilities.
The project team plays a crucial role even after deployment. They should remain actively involved in monitoring system performance, resolving issues, and supporting new business needs as they emerge. Regular maintenance and timely adoption of ERP updates not only ensure compliance, but also help your organization stay competitive and get the most out of your ERP investment.
Best Practices for ERP Implementation and Management
ERP projects are infamous for exceeding budgets once the implementation phase begins. According to a recent ERP survey, 31% of respondents reported their ERP implementation took longer than expected, while 12% stated that their projects experienced significant delays. To avoid ERP implementation delays, we have highlighted best practices to keep your project on track.
Create a Clear Roadmap
One of the reasons cited for implementation delays is unclear scope and business processes. Although ERP systems connect the physical world with digital, it is typical for the business discovery process to be done manually—a time-consuming and error-prone process. IT leaders may rely on interviews with the people involved in executing the process to gather baseline data. A clear scope is critical for successful ERP implementation.
How Opkey can help: Opkey’s purpose-built ERP lifecycle optimization platform contains built in Argus AI which is based on proprietary small language model (SLM). Argus AI is trained on knowledge developed over the years within the core Opkey platform. Leveraging advanced process mining and observability, Opkey’s Configuration Agent is a powerful ERP-specific agentic AI solution that effortlessly assists with configuration to simplify complex, time-sensitive deployment work streams, reducing both cost and risk.
Don’t Underestimate Change Management
According to McKinsey, more than 70% of all digital transformation projects fail. One of the biggest reasons for ERP failure is inadequate adoption by end users. Careful planning is required to ensure users are prepared to start using new systems and processes, which means prioritizing user acceptance testing (UAT) as part of the change management required for success. Effective UAT provides business users the chance to learn and operate the ERP before going live. However, UAT is time-consuming and usually performed by business users whose plates are already full.
How Opkey can help: Opkey’s AI-enabled, no-code test automation platform empowers your team to validate software functionality with unparalleled ease and precision. Leveraging Opkey’s AI capabilities, both technical and non-technical staff can create and maintain test scripts. Opkey’s AI agents also help you with a wide variety of tasks including planning and support tickets.
Learn more: A Comprehensive Guide to User Acceptance Testing Across ERP Environments
Don’t Underestimate Support and Training
Some members of the project team might view the go-live date as the final milestone of the ERP implementation. However, for the end users, it marks the beginning of their real journey with the system. What follows deployment is crucial to ensuring the long-term success of the project. That’s why thorough end-user training is essential—employees must feel confident and capable of using the new system, especially once external consultants are no longer available for support.
How Opkey can help: Opkey’s Training Agent is an integrated change manager and end-user enablement expert, engineered to maximize end-user adoption. Leveraging end-to-end test case data and generative AI, Opkey’s Training Agent automates the user guide creation to ensure continuous training and readiness. To guide users through unfamiliar or complicated processes, the agent actively monitors user journeys and offers personalized in-app nudges.
Don’t Ignore ERP Updates
Enterprise Resource Planning updates are essential and ignoring them can have serious consequences. Leading ERP vendors such as Oracle, Workday, and Microsoft typically release updates on a quarterly, tri-annual, or bi-annual basis. Considering that most ERP implementations take six months or more, organizations must prepare for ongoing updates even during the implementation phase.
Test automation should be included in the ERP implementation plan. Integrating test automation early in the process not only helps keep the ERP implementation on schedule but also ensures long-term maintainability and smooth adoption of future updates.
How Opkey can help: Opkey’s Testing Agent revolutionizes ERP testing, reducing downtime and disruption for both business-as-usual changes and patch updates. Leveraging process mining, observability, predictive analytics, and built-in intelligence, Opkey’s Testing Agent can sense a business process change and create a risk-based test suite and can execute it autonomously. Moreover, with AI-powered self-configuring test scripts and comprehensive pre-built test scripts, the Testing Agents enable you to continuously test and validate while eliminating costly testing alternatives.
Learn more: How Agentic AI Reduces Costs in ERP Applications Deployment and Maintenance
Post-Implementation Support
ERP implementation is not a one-off effort that ends when the new system goes live. It requires regular maintenance such as fixing issues and supporting new requirements as they come up. All this can lead to high bills as businesses often use a software vendor services team or external consultants when internal resources are limited.
How Opkey can help: The Opkey Support Agent delivers real-time, intelligent assistance to end users at scale, increasing productivity and reducing costly support load. When a user creates a support request, Opkey’s Support Agent performs a complexity check. Based on the level of complexity, the agent either guides the user toward a solution using in-app prompts or further analyzes the ticket data, examining the incident timeline and detecting any patterns.
Opkey – Your Unfair Advantage for Unbeatable Test Automation
Opkey is leading the agentic AI revolution in the ERP space. Built on years of real-world ERP expertise, our ERP Lifecycle Optimization Platform is the first of its kind to maximize the power of agentic AI. Leveraging an ERP-specific small language model, combined with advanced process mining, observability, intelligent web automation, and a “human in the loop” methodology, we’ve developed a full digital workforce of specialized agentic AI agents.
ERP Lifecycle Management
Want to learn how Opkey supports ERP Lifecycle Management? Book demo